题目描述
Link
Solution
前置知识:导数
你需要了解导数的含义和一些初等函数的导数。
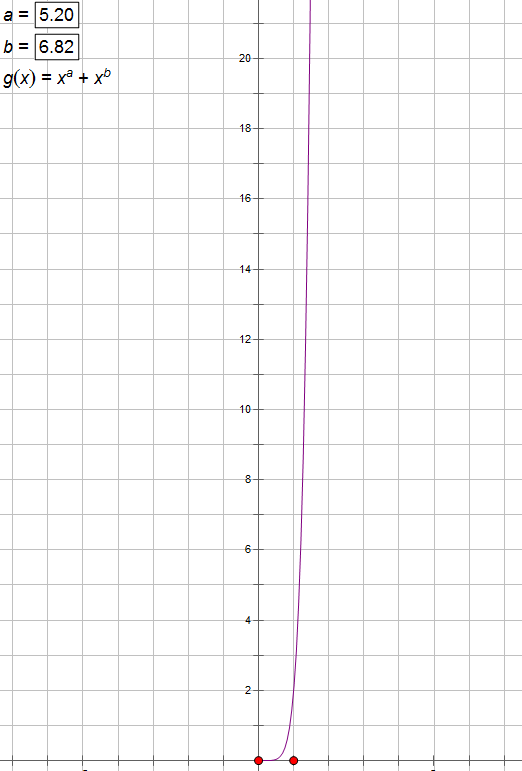
让我们先来用几何画板模拟一下这个题中的一个函数。
![]()
我们会发现如果 $a,b$ 都在所归定的数据范围内,这个函数图像形状很像二次函数,并且这个函数增长速度非常快。
我们设满足题意的最小 $n’$ 为 $a_1$ ,满足题意的最大 $n’$ 为 $a_2$。
所以 $f(a_1) - f(a_2) < 1$。
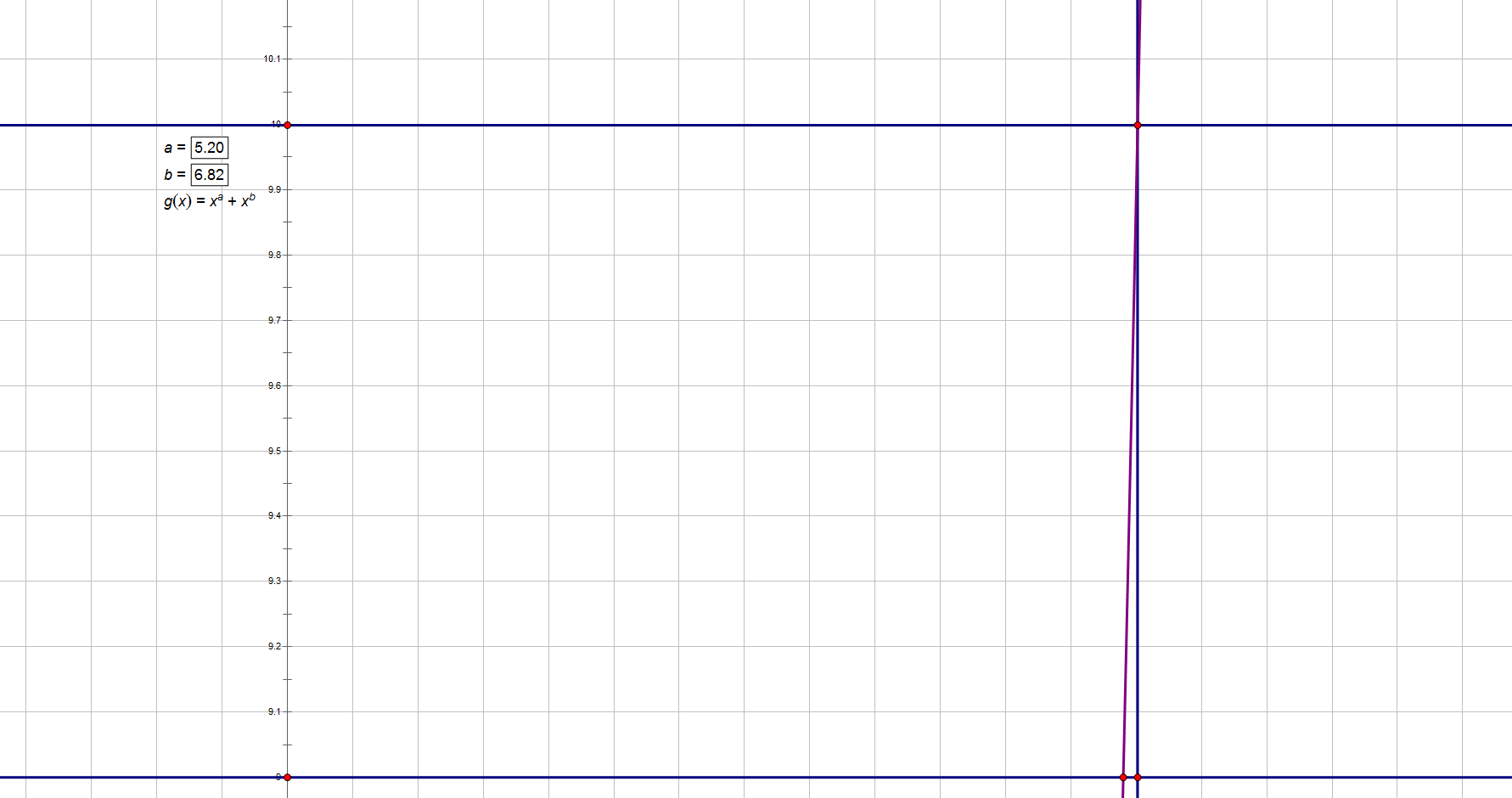
我们可以任取两个 $f(a_1),f(a_2)$ 来观察一下。
![]()
又可以发现这几个点围成了一个三角形的图案。
可能这时候有人会说:函数图像明明是曲线啊,怎么可能会是直线呢?
是的,确实是曲线,但是,用题目中所给的数据计算的话,得出的答案很大,已经到了可以忽略曲率的地步,并且题目要求的精度也不高,所以我们能够直接把这段函数图像看成直线。
但是为题又来了,该如何求它的斜率呢?
这时候,我们就需要用到导数了!
因为导数所求的是在函数任意一点处的斜率,而又因为 $f(n)$ 一定在这段函数图像上,所以我们可以直接把 $f’(n)$ 当做这个三角形斜边的斜率。
最后就可以得出答案 $a_2 - a_1 = \frac{0.999}{f’(n)}$。
上代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
namespace Mker {
#define uint unsigned int
uint sd;
int op;
inline void init() {
scanf("%u %d", &sd, &op);
}
inline uint uint_rand() {
sd ^= sd << 13;
sd ^= sd >> 7;
sd ^= sd << 11;
return sd;
}
inline double get_n() {
double x = (double) (uint_rand() % 100000) / 100000;
return x + 4;
}
inline double get_k() {
double x = (double) (uint_rand() % 100000) / 100000;
return (x + 1) * 5;
}
inline void read(double &n,double &a, double &b) {
n = get_n();
a = get_k();
if (op) b = a;
else b = get_k();
}
}
using namespace Mker;
int T;
double n, a, b, k, ans;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
init();
while (T--) {
read(n, a, b);
k = a * pow(n, a - 1) + b * pow(n, b - 1);
ans += 0.9999999 / k;
}
printf("%0.5f", ans);
}
|